Are you experiencing a persistent feeling of blockage in your ear even after undergoing microsuction? In this article, we will explore the common reasons for ear blockage, how microsuction is performed, and the possible side effects of this procedure. We will also discuss why your ear may still feel blocked after microsuction, and provide some tips on what you can do to alleviate the discomfort. Stay tuned to find out more about this common issue and how to address it effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Even after microsuction, ear blockage can persist due to incomplete removal of ear wax, lingering infection, or underlying eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Possible side effects of microsuction include pain or discomfort and dizziness, but these are usually temporary and mild.
- If your ear still feels blocked after microsuction, follow up with your audiologist and consider using ear drops, nasal decongestants, or other treatment options to address the underlying issue.
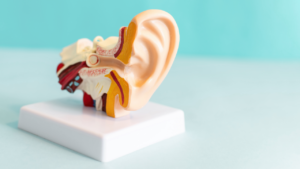
What Is Microsuction?
Microsuction is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove excess ear wax and debris from the ear canal, ensuring optimal hearing health.
By using a tiny vacuum-like device, trained professionals can gently and effectively suction out ear blockages without causing discomfort or harm to the delicate ear structures. One of the key benefits of microsuction is its precision, allowing for targeted removal of specific areas of build-up. This method also reduces the risk of pushing wax deeper into the ear canal or damaging the eardrum, which can occur with other methods like ear syringing.
When compared to traditional earwax removal techniques, microsuction is considered safer and more efficient, with minimal risk of infection or complications. Success rates are typically high, with many patients experiencing immediate relief and improved hearing after the procedure.
Regular microsuction treatments play a vital role in maintaining proper hearing function by preventing wax build-up that can lead to hearing loss, discomfort, and even ear infections. It is recommended for individuals who frequently produce excess earwax or those with narrow ear canals that are prone to blockages.
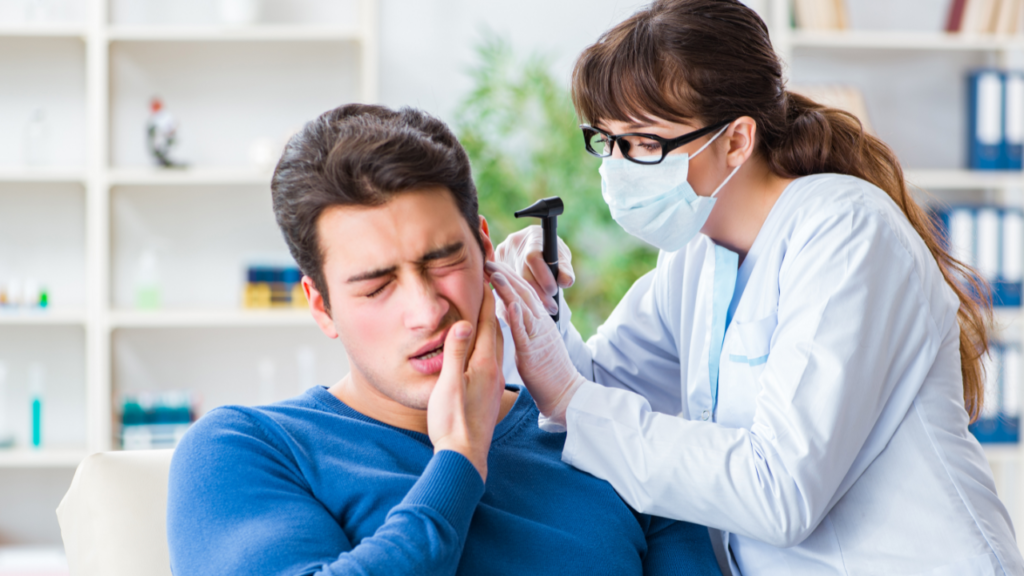
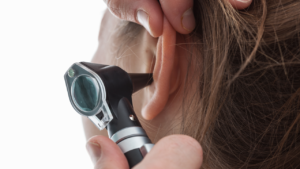
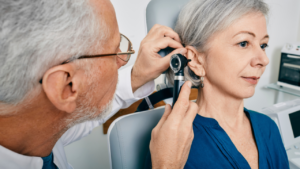
How Is Microsuction Performed?
Microsuction is typically performed by trained professionals in a clinical setting using specialised equipment to gently remove ear wax build-up from the ear canal.
Upon arrival at the clinic, the patient is usually greeted by a receptionist and guided to the treatment room. The medical professional explains the procedure and answers any questions to ensure the patient feels comfortable.
Microsuction involves the use of a binocular microscope, a suction device, and small tools called Jobson Horne probes or curettes to carefully extract the earwax. The binocular microscope provides magnification and visibility, allowing the specialist to perform the procedure with precision.
Before starting, the expert ensures that the equipment is sanitized, and the patient’s ear is examined for any signs of infection or obstruction that may require alternative treatment.
What Are The Common Reasons For Ear Blockage?
Ear blockage can occur due to various reasons, including ear wax build-up, ear infections, and underlying conditions such as gene therapy breakthroughs.
Ear wax accumulation is a common culprit for ear blockage. When the ear produces more wax than it can naturally expel, it can harden and block the ear canal. This blockage can lead to muffled hearing and discomfort.
Similarly, ear infections can cause inflammation and fluid build-up, further obstructing the ear canal. Untreated infections may result in temporary or permanent hearing loss. On the other hand, advancements in treatments such as gene therapy offer promising solutions for addressing underlying genetic conditions that can impact hearing. Timely intervention is crucial to prevent long-term complications and preserve hearing abilities.
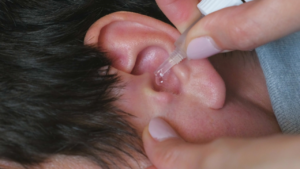
Ear Wax Buildup
Ear wax build-up, also known as cerumen impaction, can lead to hearing difficulties and discomfort, often requiring medical intervention for safe and effective removal.
When ear wax accumulates, it can create a blockage in the ear canal, affecting sound conduction and potentially leading to temporary hearing loss or tinnitus. Preventing ear wax from becoming impacted is crucial to maintaining optimal auditory health.
Individuals who use hearing aids, earplugs, or earphones are more prone to excessive wax build-up due to these devices obstructing natural wax migration. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms such as ear pain, fullness, or decreased hearing, as they can determine the appropriate treatment, which may include irrigation, suction, or manual removal with specialised instruments.
Ear Infection
Ear infections, such as otitis externa or middle ear infections, can cause blockages and discomfort, often requiring specialised procedures like irrigation to clear the ear canal.
When left untreated, these infections can lead to significant complications, including damage to the delicate structures of the ear and potential hearing loss. Infections that affect the middle ear can cause fluid build-up behind the ear drum, leading to pain, pressure, and sometimes even temporary hearing impairment.
Procedures like irrigation are essential for removing excess wax, debris, or pus trapped inside the ear canal, providing relief from symptoms and preventing further complications.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction can result in ear blockages, affecting hearing and balance, with treatments ranging from high-pressure water irrigation to specialised interventions for hearing loss.
Eustachian tube dysfunction occurs when the tube, responsible for regulating air pressure and draining fluid from the middle ear, becomes blocked or fails to open properly. This dysfunction can lead to a build-up of fluid, causing ear blockages and impacting the transmission of sound waves, resulting in hearing issues. The imbalance in pressure due to Eustachian tube dysfunction can also affect the equilibrium of the inner ear, potentially causing dizziness and balance problems.
What Is The Purpose Of Microsuction?
The primary purpose of microsuction is to effectively remove impacted ear wax, alleviating symptoms like hearing loss and discomfort, typically through a scheduled appointment with a healthcare professional.
Microsuction is a procedure commonly utilised by ear specialists to delicately extract ear wax build-up, ensuring optimal ear hygiene while restoring auditory function. By employing specialised tools and a microscopic lens for precision, microsuction offers a safer and more efficient alternative to traditional ear syringing methods. Timely appointments for microsuction are crucial in preventing complications such as infection and further blockage within the ear canal, fostering better hearing outcomes and overall ear health.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Microsuction?
Whilst microsuction is generally safe, some potential side effects may include mild discomfort, dizziness, or rare instances of irritation due to water irrigation techniques used during the procedure.
It is crucial for trained professionals to perform microsuction to minimise risks associated with the procedure. To enhance patient safety, practitioners ensure that the water irrigation method is controlled and gentle, reducing the likelihood of any adverse effects. In case a patient experiences discomfort or dizziness during the procedure, the practitioner will pause to allow the individual to recover before resuming. Irritation due to water irrigation is typically managed by applying soothing solutions or recommending post-procedure care to alleviate any temporary discomfort.
Pain or Discomfort
One of the common side effects of microsuction may involve mild pain or discomfort during the ear wax removal process, which is typically managed by experienced professionals for patient comfort.
Effective pain management techniques are crucial in ensuring that patients experience minimal discomfort during the procedure. Healthcare providers skilled in the art of microsuction understand the delicate nature of the ear canal and employ gentle manoeuvres to reduce any potential pain. They may also use specialised numbing agents or techniques to further alleviate discomfort, ensuring a smooth and tolerable experience for the patient.
Dizziness
Dizziness can occasionally occur post-microsuction due to changes in ear pressure or fluid displacement, a sensation that may be transient and should be reported to healthcare providers if persistent.
During microsuction, the delicate inner ear structures may be momentarily disturbed, leading to a temporary imbalance in fluid pressure. This can trigger feelings of dizziness as the body adjusts to the new equilibrium. Ear wax removal through microsuction can sometimes dislodge blockages that have been affecting the inner ear, further contributing to this sensation. While these symptoms are usually short-lived and resolve on their own, patients should still maintain vigilance.
Why Does My Ear Still Feel Blocked After Microsuction?
Persistent ear blockage post-microsuction may be attributed to factors like incomplete removal of ear wax, underlying ear infections, or potential hearing issues, necessitating further evaluation such as a hearing test.
Residual ear wax left behind after microsuction can cause blockages, as even small amounts can significantly impair hearing. Infections, such as otitis media, can lead to fluid build-up in the middle ear, contributing to the sensation of fullness or blockage. Underlying hearing conditions like otosclerosis or Meniere’s disease may also manifest as persistent ear blockage.
Follow-up assessments after microsuction are crucial for a comprehensive evaluation, enabling healthcare professionals to identify the exact cause and provide targeted treatment, which might include the use of ear drops, antibiotics, or hearing aids.
Incomplete Removal of Ear Wax
Incomplete removal of ear wax during microsuction can lead to residual blockages, prompting the use of softening agents like olive oil to facilitate the complete clearance of wax.
Residual blockages left untreated can cause discomfort, hearing impairment, and even increase the risk of ear infections. Using softening agents such as olive oil helps break down the hardened wax, making it easier to remove through natural processes or professional intervention.
Simply relying on softening agents may not suffice, as proper cleaning techniques are crucial to prevent further accumulation of wax. Regularly cleaning the ears with gentle methods can help maintain optimal ear health and reduce the likelihood of recurring wax issues.
Ear Infection Persisting
Persistent ear infections post-microsuction may indicate deeper issues with the ear drum or residual bacterial growth, requiring treatments such as urea peroxide drops or medical intervention to address the infection.
When left untreated, these infections can pose serious risks to the delicate structures inside the ear, possibly leading to complications such as hearing loss, vertigo, or even more severe damage to the ear drum. The failure to address persistent bacterial growth can result in chronic inflammation, pain, and recurrent infections, significantly impacting the individual’s quality of life.
Specialised treatments like urea peroxide drops play a crucial role in breaking down the biofilm formed by bacteria in the ear canal, aiding in the eradication of stubborn infections that traditional antibiotics may struggle to target effectively.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Not Addressed
Untreated Eustachian tube dysfunction can contribute to ongoing ear blockage and symptoms like tinnitus, underscoring the importance of targeted interventions or procedures to address the underlying dysfunction.
When Eustachian tube dysfunction is left untreated post-microsuction, the repercussions can be significant. The persistent blockages in the ear can lead to discomfort, impaired hearing, and a feeling of fullness in the ear, affecting one’s quality of life.
In addition, tinnitus, often described as ringing or buzzing in the ears, can manifest and exacerbate the already distressing situation. This highlights the necessity of promptly treating Eustachian tube dysfunction to prevent such ongoing issues.
Specialised procedures or therapies may be required for effective management of the dysfunction, tailored to each individual’s specific condition. Consulting with a healthcare professional experienced in ear disorders is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
What Can I Do If My Ear Still Feels Blocked After Microsuction?
In cases of persistent ear blockage post-microsuction, individuals can seek further assistance by scheduling a follow-up appointment, using ear drops, considering high-pressure water irrigation, or exploring alternative treatment options.
For those experiencing ongoing discomfort following microsuction, utilising ear drops can help soften any remaining earwax and facilitate its natural expulsion. Attending follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional is crucial to monitor progress and address any underlying issues.
In more stubborn cases, high-pressure water irrigation may be recommended to dislodge stubborn blockages. It is essential to note that these procedures should only be performed by trained professionals to prevent any damage to the delicate ear canal.
Remember, personalised solutions tailored to individual needs are key in effectively managing ear blockages post-microsuction. It’s vital to communicate openly with your healthcare provider to find the most suitable course of action for your specific situation.
Follow up with your audiologist
Scheduling a follow-up appointment with your audiologist or GP can help address persistent ear blockage concerns post-microsuction, allowing for further assessment of hearing issues or underlying conditions.
These follow-up appointments play a crucial role in monitoring your ear health progress and ensuring any potential complications are detected early. During these appointments, the healthcare professionals can perform comprehensive evaluations, including hearing tests and otoscopic examinations, to assess your auditory system’s functionality.
The audiologist or GP may provide personalised advice on proper ear care practices to prevent future blockages or further damage to your ears. Regular follow-ups are essential in maintaining optimal ear health and preventing long-term issues associated with untreated hearing loss or related conditions.
Use Ear Drops
Ear drops containing ingredients like sodium bicarbonate can help soften residual ear wax post-microsuction, facilitating natural clearance and alleviating sensations of blockage.
When residual wax is left in the ear after a microsuction procedure, it can lead to discomfort or mild blockage. The introduction of specially formulated ear drops can support the body’s natural process of wax removal. Sodium bicarbonate, a key ingredient in many ear drop solutions, works by breaking down wax buildup, making it easier to evacuate naturally. Proper application of these drops, with a gentle massage of the ear canal, can further enhance the softening process and promote effective wax expulsion.
Try Nasal Decongestants
Nasal decongestants can sometimes aid in relieving ear blockages by reducing congestion and pressure, a complementary approach to high-pressure water irrigation or suction techniques in persistent cases.
In cases where ear blockages are caused by inflammation of the Eustachian tube or nasal congestion, using nasal decongestants can help alleviate the underlying issues. By shrinking swollen nasal passages and reducing mucus production, nasal decongestants can indirectly alleviate pressure imbalances that affect the ear canal. This, in turn, can facilitate the success of high-pressure water irrigation or suction methods by prepping the ear canal for effective clearing.
Consider Other Treatment Options
Exploring alternative treatment options at specialised clinics or under NHS care can provide comprehensive solutions for persistent ear blockages not resolved by microsuction alone, ensuring thorough evaluation and tailored interventions.
Specialised clinics and NHS services offer various advanced approaches for managing stubborn ear blockages, such as irrigation procedures, steroid treatments, or surgical interventions.
These institutions are equipped with the necessary expertise and equipment to address complex cases that require a more nuanced strategy.
Individualised care plans are crucial in these situations, as they consider the unique needs and conditions of each patient to ensure the most effective outcome.