Do you ever wonder what exactly ear wax is and why it needs to be removed? Excessive ear wax buildup can lead to a variety of issues, including dizziness. In this article, we will explore the process of ear wax removal, the signs of buildup, and how it can cause dizziness. We will also discuss how to prevent dizziness during the removal process and the potential complications that can arise if not done correctly. Stay tuned to learn more about this common but often overlooked aspect of ear health.
Key Takeaways:
- Excessive ear wax buildup can lead to various symptoms, including dizziness.
- Dizziness during ear wax removal is not uncommon and can be caused by various factors.
- There are ways to prevent dizziness and minimise the risk of complications during ear wax removal, such as staying still during the procedure and seeking professional help.
What Is Ear Wax?
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the ear glands to keep the ear canal lubricated and protect the ear from dust, bacteria, and other external agents.
Ear wax is composed of a combination of secretions from ceruminous glands, sweat glands, and dead skin cells. This waxy material forms a protective barrier that prevents water from entering the ear canal, which can cause infections. Along with its protective role, ear wax also helps to clean and lubricate the ear, promoting overall ear health.
What Is Ear Wax Removal?
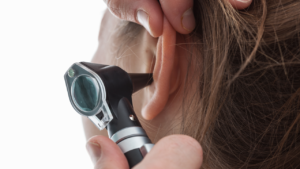
Ear wax removal is a procedure carried out by a healthcare professional to eliminate excess or impacted ear wax from the ear canal, improving hearing and reducing the risk of complications.
The ear canal naturally produces wax to protect the ear from dust and foreign particles. A build-up of wax can lead to hearing difficulties, earaches, and even infections.
Seeking professional help for ear wax removal is essential to avoid damaging the delicate structures of the ear. Healthcare providers use specialised tools and techniques to safely remove the wax without causing harm.
Attempting to remove ear wax at home with cotton buds or other objects can push the wax further into the ear, resulting in more serious issues. Therefore, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper assessment and treatment.
Why Is Ear Wax Removal Necessary?
Ear wax removal becomes necessary when there is a build-up of cerumen in the ear canal, leading to symptoms such as hearing loss, vertigo, and balance issues due to impacted ear wax.
Excessive wax accumulation can not only impair hearing but also disrupt the delicate equilibrium maintained by the balance organs in the inner ear. When ear wax blocks the ear canal, it can interfere with the transmission of sound waves, creating a muffled effect that impacts one’s ability to clearly perceive sounds. The pressure from the wax build-up can cause dizziness and vertigo, affecting the functionality of the balance organs like the semicircular canals.
What Are The Signs Of Excessive Ear Wax Buildup?
Excessive ear wax build-up can manifest through various symptoms, including hearing loss, earache, tinnitus, and a sensation of fullness in the ear.
One of the common signs signalling the accumulation of excessive ear wax is the gradual decrease in hearing clarity. This occurs when the wax blocks the ear canal, hindering sound waves from reaching the eardrum effectively. Individuals might experience earaches or a persistent buzzing in the ears known as tinnitus due to wax build-up. If left unaddressed, this can lead to increased susceptibility to ear infections. Seeking professional advice and possibly undergoing a hearing test can help determine the extent of the wax build-up and guide appropriate treatment measures.
How Is Ear Wax Removal Done?
Ear wax removal can be carried out through different methods such as ear irrigation, suction, or curettage, depending on the severity of the earwax blockage and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.
Ear irrigation, also known as ear syringing, involves using a gentle stream of water to flush out the ear canal and dislodge the wax. This method is commonly used in clinics and can be effective in clearing out excess wax buildup.
Suction removal, on the other hand, uses a specialised tool to suction out the wax from the ear canal. This method is precise and can be particularly useful for stubborn or hard-to-reach earwax blockages.
Another technique, known as curettage, involves using a small scoop-like instrument called a curette to carefully scrape away the earwax. This method is often used when the wax is impacted and difficult to remove through other means.
Ear Irrigation
Ear irrigation is a common method of ear wax removal that involves flushing the ear canal with a gentle stream of warm water to dislodge and remove the wax build-up.
During the ear irrigation procedure, the water pressure created by the stream of warm water helps to soften the earwax, making it easier to flow out of the ear canal. The water used in ear irrigation is typically at body temperature to prevent any discomfort or damage to the delicate tissues in the ear. It is essential to ensure that the water pressure is carefully regulated to avoid any complications such as dizziness, vertigo, or in rare cases, rupture of the eardrum.
Suction
Suction, including microsuction, is a method of ear wax removal that uses suction devices to extract excess wax from the ear canal safely and efficiently.
When utilising this technique, the specialised devices create a gentle suction force that aids in dislodging and removing stubborn ear wax without causing any discomfort or harm.
Microsuction, a precise form of suction, is particularly effective as it allows healthcare professionals to have a clear view of the ear canal through a magnifying lens or microscope, ensuring accurate removal.
If there are concerns about potential complications, such as a perforated eardrum, diagnostics like otoscopy or tympanometry are commonly performed to assess the condition before proceeding with the suction procedure.
Curettage
Curette is a procedure for ear wax removal that involves the use of a curette or a specialised tool to carefully scoop out impacted wax from the ear canal, minimising the risk of complications.
During curette, a healthcare professional uses the instrument to navigate the ear canal, gently removing the wax buildup that can cause discomfort and hearing issues if left untreated. This treatment is known for its precision in targeting specific areas where wax is impacted, ensuring a thorough removal. The procedure typically takes place in a clinical setting where the professional can closely monitor and perform the process safely. Patients often experience relief and improved hearing clarity after a successful ear wax removal via curette.
Can Ear Wax Removal Cause Dizziness?
In some cases, ear wax removal procedures may lead to temporary dizziness or vertigo as a result of the stimulation of the balance organs within the inner ear.
When earwax builds up in the ear canal, it can interfere with the normal functioning of the balance organs called semicircular canals, which are responsible for maintaining equilibrium. The removal process can sometimes trigger the delicate system, causing a brief feeling of dizziness or imbalance. This sensation often subsides as the inner ear recalibrates, but individuals with severe blockages or underlying vestibular issues may experience prolonged dizziness or vertigo. It is crucial to have earwax removed safely by a healthcare professional to minimise the risk of such disturbances and maintain optimal ear health.
What Causes Dizziness During Ear Wax Removal?
Dizziness during ear wax removal can be caused by the manipulation of the ear canal, stimulation of the vestibular system, or changes in body temperature and pressure during the procedure.
When ear wax is being removed, the delicate balance mechanisms in the inner ear can be disrupted, leading to signals being misinterpreted by the brain, resulting in dizziness. For individuals already experiencing hearing loss or suffering from an ear infection, the removal process can exacerbate these conditions, further impacting balance and equilibrium.
How Common Is Dizziness During Ear Wax Removal?
Dizziness during ear wax removal is relatively uncommon but can occur in sensitive individuals or those with pre-existing balance issues, leading to temporary sensations of vertigo or unsteadiness.
Despite its rarity, it is essential for healthcare providers performing ear wax removal procedures to be cautious and prepared for any potential side effects.
Individuals with vertigo or balance disorders may be more prone to experiencing dizziness due to the manipulation of the ear canal during the removal process. Proper assessment of the patient’s medical history and symptoms beforehand can help in minimising the risk of dizziness episodes. In most cases, the sensations are short-lived and resolve once the procedure is complete.
How To Prevent Dizziness During Ear Wax Removal?
Preventing dizziness during ear wax removal involves staying still during the procedure, using ear drops beforehand to soften the wax, and seeking guidance from a healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective removal.
One useful technique to minimise dizziness is to maintain a steady posture throughout the process, as sudden movements can exacerbate the sensation.
Applying ear drops before the removal helps in loosening the wax, making it easier to extract.
If you experience persistent dizziness, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and possible treatment options, such as ear syringing which employs gentle water pressure to flush out the obstruction in a controlled manner.
Stay Still During The Procedure
Remaining still during ear wax removal is crucial to prevent unnecessary movements that could potentially aggravate the balance organs and lead to feelings of dizziness or vertigo.
When the delicate structures within the inner ear, responsible for maintaining balance and equilibrium, are disturbed by sudden motions, it can cause dizziness or vertigo sensations. By staying motionless, the risk of disrupting these intricate systems is significantly reduced.
Unnecessary movements can also interfere with the delicate process of extracting ear wax. This procedure requires precision and focus, both of which can be compromised if the patient is not completely still. Therefore, maintaining stillness is not only important for comfort but also for the overall success and safety of the ear wax removal process.
Use Ear Drops Before The Procedure
Applying ear drops before ear wax removal can help soften the wax, making it easier to remove and reducing the likelihood of complications or discomfort during the procedure.
By introducing ear drops into the ear canal, the drops work to break down the hardened ear wax, loosening its grip on the ear canal walls. This softening process not only facilitates the removal of wax but also helps to prevent potential injury or irritation that may occur during the extraction process. The use of certain drops, such as those containing hydrogen peroxide, can also have a cleansing effect, reducing the risk of developing an ear infection post-procedure.
Seek Professional Help
Consulting a healthcare professional for ear wax removal is essential to ensure the safe and effective elimination of wax build-up while minimising the risk of complications or adverse reactions.
Healthcare providers possess the necessary training and tools to accurately assess the condition of the ears and determine the most suitable method for wax removal. Attempting to remove ear wax at home using improper tools or techniques can lead to injury or further impaction, potentially causing damage to the ear canal or eardrum.
Professional assistance guarantees a thorough examination and customised approach, taking into account individual variations in ear anatomy and wax consistency. Healthcare professionals can identify underlying issues and provide appropriate treatment if necessary, safeguarding the overall health of the ear.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Ear Wax Removal?
Complications of ear wax removal may include damage to the ear canal, risk of infection, and potential hearing loss if the procedure is not conducted carefully or by a trained healthcare professional.
Perforated eardrum is a serious risk that can occur if improper tools or techniques are used during the removal process. The delicate nature of the eardrum makes it vulnerable to injury, leading to pain, dizziness, and even permanent hearing impairment. Seeking guidance from a qualified healthcare provider is crucial to minimise these risks and ensure a safe and effective procedure. It is essential to avoid using cotton buds, as they can push the wax deeper into the ear canal, exacerbating the problem and potentially causing damage.
Damage To The Ear Canal
Damage to the ear canal during wax removal can occur due to excessive force, improper tools, or lack of expertise, leading to injuries, pain, and potential complications that require medical attention.
One of the crucial risks associated with ear canal damage is the possibility of developing an ear infection, which can exacerbate discomfort and impede hearing function.
Professional care and gentle techniques are essential when addressing ear wax buildup to mitigate the chances of complications. In some cases, ill-advised practices like ear syringing can further elevate the risk of injury, making it imperative to seek guidance from trained professionals for safe and effective wax removal. Understanding the delicate nature of the ear canal is paramount in avoiding unnecessary harm and promoting overall ear health.
Infection
Infections following ear wax removal can occur if bacteria enter the ear canal during the procedure, highlighting the importance of sterile techniques and post-procedural care by a healthcare professional.
Preventative measures, such as using sterile instruments and proper hygiene practices, play a crucial role in minimising the risk of infection. Health care professionals are trained to follow strict guidelines to ensure a safe and clean procedure, reducing the chances of complications.
It’s essential to seek professional help for ear wax removal rather than attempting it at home, as improper techniques or tools can lead to injury or infection. Early detection of any signs of infection, such as increased pain, swelling, or discharge, is key to prompt treatment and prevention of further complications.
Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be a complication of ear wax removal, particularly if the procedure dislodges impacted wax or causes damage to the delicate structures of the ear, leading to temporary or permanent impairment.
It is crucial to take precautions while attempting to remove ear wax to minimise the risk of hearing damage. Using cotton buds or other objects to clean the ears can push wax deeper inside, potentially leading to impaction. In cases of impacted wax, seeking professional help is advisable to avoid accidental injury to the eardrum. Ear infections can also result from improper wax removal techniques, affecting hearing and balance. Regular ear check-ups with a healthcare provider can help prevent complications associated with ear wax management.