Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the ears to protect and clean the ear canal. But what happens if this wax is not removed properly? Impacted ear wax can lead to a variety of issues such as hearing loss, ear infections, and even tinnitus.In this article, we will explore the symptoms of impacted ear wax, how it can be removed, and most importantly, how to prevent build-up in the first place. So, let’s dive in and learn more about the importance of ear wax maintenance.
Key Takeaways:
- Ear wax serves as a protective barrier for the ear canal, preventing dirt and bacteria from entering.
- If ear wax is not removed, it can lead to various issues such as impacted ear wax, hearing loss, ear infections, and tinnitus.
- To prevent ear wax build up, avoid using cotton swabs, use earplugs in water, and keep the ear canal dry.
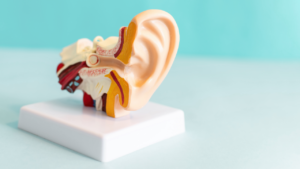
What Is Ear Wax?
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal to protect the ear from dust, foreign particles, and microbial infections.
Its primary function lies in creating a protective barrier that traps debris, preventing it from reaching the delicate structures within the ear. The texture of ear wax can vary from individual to individual, depending on factors such as genetics and hygiene practices. Some people may have dry and flaky wax, while others produce a more moist and sticky consistency.
The production process of ear wax involves a continuous secretion by the ceruminous glands, combined with the migration of skin cells from the ear canal lining. This process helps to naturally clean the ear canal and maintain its health.
What Is The Purpose Of Ear Wax?
The primary purpose of ear wax is to lubricate and protect the ear canal, ensuring proper function and health while preventing the entry of harmful debris or pathogens.
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, plays a vital role in maintaining ear health through its protective properties. It acts as a natural barrier against foreign particles, insects, and water, safeguarding the delicate structures of the ear from damage or infections.
Plus its protective function, ear wax also helps in regulating moisture levels within the ear canal. By retaining an optimal amount of moisture, it prevents dryness or irritation, contributing to the overall comfort and health of the ear.
Regular monitoring of ear wax by healthcare providers is essential to ensure its presence in appropriate amounts. Excessive wax buildup can lead to issues such as hearing loss, earaches, or tinnitus, highlighting the importance of timely removal when necessary.
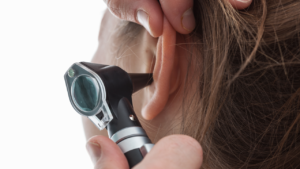
How Is Ear Wax Removed?
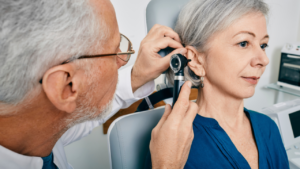
Ear wax can be removed through various methods, including ear irrigation, ear curettes, and the use of ear drops designed to soften and facilitate the removal of excess wax.
Ear irrigation, also known as ear syringing, involves flushing the ear canal with a gentle flow of water to dislodge and remove the wax buildup. This method is commonly performed by healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective wax removal.
On the other hand, ear curettage, using specialised instruments called curettes, is a manual technique where the wax is carefully scraped out under direct visualization. Ear drops containing carbamide peroxide or hydrogen peroxide can be used to soften the wax over a period of a few days before being flushed out during irrigation.
Ear Irrigation
Ear irrigation is a common method used by healthcare providers, such as pharmacists, to flush out excessive ear wax buildup and alleviate symptoms such as earache and hearing loss.
During the process of ear irrigation, a specialised device known as an ear syringe or irrigation kit is typically utilised to introduce a gentle stream of warm water into the ear canal. The warm water helps soften the earwax, making it easier to remove. Providers ensure the water temperature is safe to prevent any discomfort or damage to the delicate ear structures.
Safe and controlled irrigation is crucial to prevent pushing the earwax further into the ear canal, which could potentially worsen the blockage. Healthcare professionals are trained to perform this procedure carefully, ensuring the safety and comfort of the patient throughout.
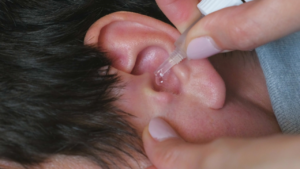
Ear Curette
An ear scoop is a specialised tool often used by ENT doctors to carefully scrape off impacted ear wax that may be causing symptoms like earache, vertigo, or tinnitus.
Impacted ear wax occurs when ear wax builds up deep inside the ear canal, causing a blockage. This blockage can lead to various uncomfortable symptoms, such as hearing loss, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and even dizziness.
- Ear scoops have a unique design that allows medical professionals to safely extract the hardened wax from the ear canal without causing damage to the delicate ear structures. By using gentle and precise movements, doctors can effectively remove the blockage and provide relief to the patient.
Ear Drops
Ear drops containing substances like olive oil or sodium bicarbonate are often recommended for softening earwax, aiding in its natural expulsion and preventing the build-up of impacted wax.
These natural ingredients have shown effectiveness in breaking down earwax, making it easier for the body to naturally remove it. Olive oil, for instance, helps to lubricate the ear canal, easing the passage of wax and reducing the risk of blockages or impactions.
Sodium bicarbonate, on the other hand, has mild effervescent properties that can help to dissolve hardened wax, promoting its gradual disintegration. Almond oil is another popular choice for its moisturising and nourishing properties, which can help soothe the delicate skin inside the ear while also aiding in the removal of excess wax.
What Happens If Ear Wax Can Not Be Removed?
When ear wax cannot be effectively removed, it may lead to complications such as impacted earwax, resulting in hearing loss or ear infections that require medical attention from a primary care doctor.
An accumulation of ear wax can block the ear canal, causing discomfort, dizziness, or ringing in the ears. Impacted earwax can also affect balance and coordination as it interferes with the natural hearing process. If left untreated, these symptoms may worsen, leading to more severe consequences like infection. Ear infections can be painful and may further impact one’s ability to hear clearly, affecting daily communication and quality of life. Seeking prompt help from a healthcare provider is crucial to prevent complications from escalating.
Impacted Ear Wax
Impacted ear wax can lead to symptoms such as persistent earache, dizziness, and reduced hearing capabilities, indicating the need for prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Earaches stemming from impacted ear wax can range from mild discomfort to sharp, stabbing pains, often exacerbated when pressure is applied to the ear.
Dizziness can occur due to the disruption in the normal functioning of the inner ear caused by the wax build-up, leading to a sense of imbalance or vertigo.
The reduced hearing capabilities associated with impacted ear wax can vary in severity, from mild muffled sounds to almost complete loss of hearing.
Hearing Loss
Persistent hearing loss, often associated with changes in earwax colour or consistency, may indicate the presence of impacted wax that requires evaluation and treatment by an ENT doctor.
Earwax build-up, medically known as cerumen impaction, can lead to a range of symptoms beyond just hearing loss. When the ear canal becomes blocked with excessive wax, it can cause earaches, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), dizziness, and even infections.
It’s crucial to pay attention to any alterations in the colour, texture, or amount of earwax as these changes can signal underlying issues that need medical attention. Regular monitoring and gentle cleaning of the ears can help prevent complications and maintain ear health.
ENT doctors, or otolaryngologists, specialise in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the ears, nose, and throat. They are equipped with the expertise and tools to safely remove impacted wax, alleviate symptoms, and restore optimal hearing function.
Ear Infections
Untreated ear wax blockages can increase the risk of ear infections, particularly in individuals with specific earwax types, highlighting the importance of prompt assessment by a pharmacist or healthcare provider.
Earwax, also known as cerumen, serves a protective function in the ear by trapping debris and preventing infections. When earwax builds up and hardens, it can lead to blockages, causing pain, hearing loss, and an increased likelihood of infection. Different individuals have varying types of earwax, ranging from wet and sticky to dry and flaky, which can impact the likelihood of blockages occurring.
To manage earwax-related issues effectively, preventative measures such as regular ear hygiene practices, using ear drops, or seeking professional cleaning may be necessary.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus, a common symptom of unresolved ear wax issues, may necessitate specialised earwax removal tools and procedures that are typically performed in a clinical setting like a GP surgery.
Earwax accumulation can lead to a range of issues, including hearing problems and the sensation of ringing in the ears, known as tinnitus. When individuals experience persistent tinnitus, it is crucial to seek professional help to address the underlying cause, which often involves the removal of excess earwax.
Within GP surgeries, healthcare providers utilise various techniques to safely remove earwax buildup. From irrigation methods to manual removal using specialised instruments, these procedures are tailored to the patient’s specific needs and the extent of the earwax blockage.
What Are The Symptoms Of Impacted Ear Wax?
The symptoms of impacted ear wax include ear pain, dizziness, fullness or pressure in the ear, and difficulty hearing, signalling the need for evaluation and treatment to alleviate discomfort and potential complications.
Ear pain associated with impacted ear wax can range from mild discomfort to sharp, stabbing sensations.
Dizziness may result from the interference of wax buildup with the proper function of the inner ear.
The sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear can be disorienting and affect balance.
Hearing difficulties may manifest as muffled sounds, difficulty understanding speech, or ringing in the ears.
Addressing these symptoms promptly is crucial to prevent worsening conditions and restore optimal ear function.
Ear Pain
Ear pain, often linked to changes in earwax colour or texture, can signify underlying issues like wax build-up, infections, or inflammation that may require prompt treatment and monitoring.
When experiencing ear pain, it is crucial to pay attention to the colour and consistency of earwax as it can provide valuable insights into the root cause of discomfort. For example, dark or discoloured earwax might indicate the presence of an infection, while dry and flaky earwax could be a sign of eczema affecting the ear canal. Seeking professional guidance from an audiologist or otolaryngologist is essential to accurately diagnose and address ear-related issues. Depending on the underlying cause, treatment options may range from simple ear drops for wax removal to antibiotics for infections or corticosteroids for inflammation.
Dizziness
Dizziness, a common symptom of impacted ear wax, can be managed through preventive measures such as using natural remedies like almond oil to soften the wax and promote its expulsion.
When excess ear wax accumulates in the ear canal, it can lead to dizziness due to the disrupted balance mechanisms in the inner ear. This can result in vertigo and a feeling of unsteadiness. To prevent these symptoms, regular ear hygiene practices and avoiding the use of cotton buds that push the wax further in are recommended.
Plus preventive strategies, almond oil is often used as a gentle and natural way to soften ear wax. Applying a few drops into the affected ear can help break down the wax and facilitate its removal, relieving dizziness and associated discomfort.
Fullness Or Pressure In The Ear
Sensations of fullness or pressure in the ear, often associated with conditions like swimmer’s ear or earwax blockages, may require professional assessment to determine the underlying causes and appropriate treatment.
Swimmer’s ear, also known as otitis externa, is an infection common among swimmers and those in humid environments. This condition occurs when water is trapped in the ear canal, providing a suitable environment for bacteria to thrive. On the other hand, earwax build-up can lead to a feeling of fullness or pressure if it accumulates and hardens, causing a blockage. Additional factors such as allergies, sinus infections, or Eustachian tube dysfunction can also contribute to these sensations that should not be overlooked.
Difficulty Hearing
Difficulty hearing, often accompanied by vertigo or imbalance, can be a sign of earwax impaction or related issues, warranting evaluation by healthcare professionals to address potential hearing loss concerns.
When earwax builds up in the ear canal, it can lead to blockages that interfere with sound transmission, affecting the ability to perceive sounds clearly. Earwax impaction can manifest in various ways, including earaches, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), or a sensation of fullness in the ear. In severe cases, blocked ear canals can trigger dizziness and balance problems, making simple tasks like walking or standing challenging. Consultation with an ENT specialist or audiologist is crucial to accurately diagnose and treat these ear-related issues for optimal hearing health.
How Can Ear Wax Build Up Be Prevented?
Preventing ear wax build up involves simple measures such as using earplugs in water, avoiding cotton buds, and maintaining ear canal hygiene to minimise the risk of blockages that may require intervention from ENT doctors.
Using earplugs while swimming or showering can prevent water and moisture from affecting the ear canal, which can contribute to wax build-up. The risk of earwax blockages increases with improper use of cotton buds, as they can push the wax deeper into the ear canal, leading to potential complications. Regular ear hygiene practices, such as gently cleaning the outer ear with a damp cloth, can help prevent excess wax accumulation and maintain healthy ear function.
Use earplugs in water
Using earplugs while swimming or showering can help protect the ear canal from excessive moisture and debris, reducing the risk of earwax accumulation and potential hearing loss concerns.
Moisture in the ear canal can create a conducive environment for bacterial or fungal growth, leading to infections or inflammation.
Earplugs act as a barrier, preventing water from entering the ear and disrupting the delicate balance within.
Regular use of earplugs can significantly reduce the chances of developing swimmer’s ear, a painful infection commonly caused by water exposure.
Proper ear hygiene, including drying ears thoroughly after water activities, complemented by earplug usage, is crucial in maintaining optimal ear health.
Avoid Using Cotton Swabs
Refraining from using cotton buds to clean the ear canal is essential to prevent earwax compaction, which can lead to earache, hearing loss, or other complications that may require medical attention.
When inserted too deeply into the ear canal, cotton buds can push the earwax further inside, causing blockages. This blockage can impair hearing and lead to discomfort or even infections.
The improper use of cotton buds increases the risk of accidental injuries within the delicate ear canal, potentially causing cuts, scratches, and in severe cases, perforated eardrums. It’s crucial to adopt safer ear cleaning practices such as using ear drops or seeking professional earwax removal by a healthcare provider to avoid these risks and maintain ear health.
Keep The Ear Canal Dry
Maintaining proper ear hygiene by keeping the ear canal dry and avoiding excessive moisture can reduce the likelihood of earwax build-up and potential complications that may necessitate intervention by a primary care doctor.
Excessive moisture in the ear canal can create an ideal environment for the accumulation of earwax, leading to blockages and discomfort. By embracing effective drying methods, such as gently patting the ears dry after swimming or showering, individuals can help prevent the excessive build-up of earwax. It is essential to avoid inserting cotton buds or other objects into the ear canal, as this can push wax deeper and cause injury.
Primary care providers play a crucial role in educating patients on proper ear care practices and addressing any concerns related to ear health.